June 13, 2024 | by Kaju
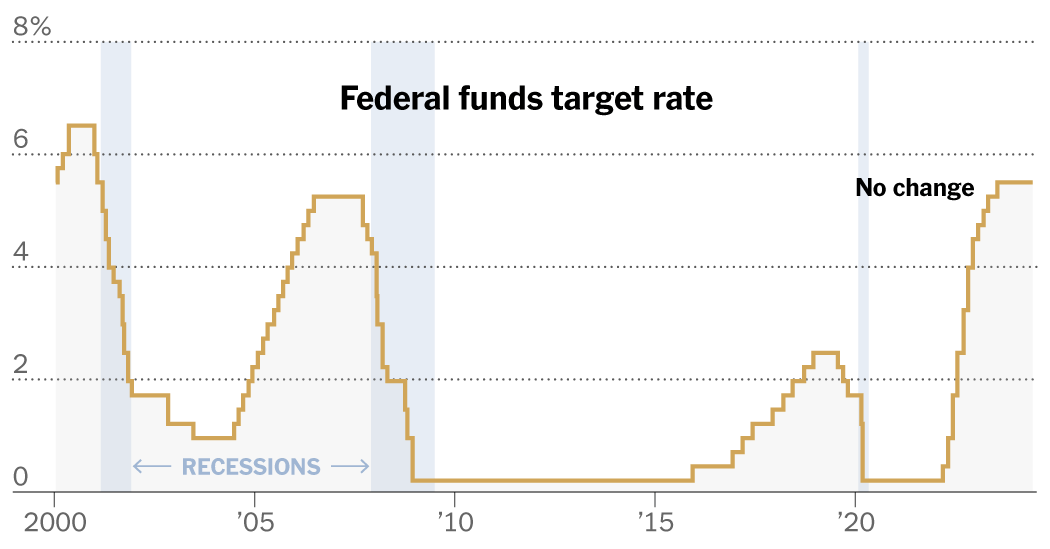
Federal Reserve officers left rates of interest unchanged at their June meeting on Wednesday and predicted that they are going to cut borrowing costs simply as soon as earlier than the top of 2024, taking a cautious method as they attempt to keep away from declaring a untimely victory over inflation.
Whereas the Fed had been anticipated to go away charges unchanged, its projections for a way rates of interest could evolve stunned many economists.
When Fed officers final launched quarterly financial estimates in March, they anticipated reducing rates of interest thrice this yr. Traders had anticipated them to revise that outlook considerably this time, in gentle of cussed inflation early in 2024, however the shift to a single lower was extra drastic.
Jerome H. Powell, the Fed chair, made clear in a postmeeting information convention that officers had been taking a cautious and conservative method after months of bumpy inflation knowledge.
With value will increase proving unstable and the job market remaining resilient, policymakers imagine they’ve the wiggle room to carry rates of interest regular to ensure they totally stamp out inflation with out operating an excessive amount of of a threat to the financial system. However the Fed chair additionally urged that extra fee cuts could possibly be attainable relying on financial knowledge.
“Fortuitously, now we have a powerful financial system, and now we have the flexibility to method this query fastidiously — and we are going to method it fastidiously,” Mr. Powell mentioned. He added that “we’re very a lot maintaining a tally of draw back financial dangers, ought to they emerge.”
Fed officers lifted rates of interest quickly between early 2022 and final July to a more-than-two-decade excessive of 5.3 %. They’ve held them there since, hoping that larger borrowing prices will gradual shopper and enterprise demand sufficient to wrestle value will increase again to a standard tempo.
Initially, the plan went superbly: Inflation slowed steadily in 2023, a lot that Fed officers entered 2024 anticipating to chop rates of interest considerably. However then value will increase proved surprisingly cussed for just a few months — and policymakers needed to delay their plans for fee cuts, afraid of reducing borrowing prices too early.
The danger in reducing prematurely is that “we might find yourself undoing a whole lot of the great that we’ve performed,” Mr. Powell defined on Wednesday.
Now the inflation image is altering once more. Recent Shopper Value Index knowledge on Wednesday urged that the early 2024 inflation stickiness was a pace bump moderately than a change within the pattern: Value will increase cooled notably and broadly in Might.
Nonetheless, it’s getting late within the yr for the Fed to drag off the three fee cuts that it had anticipated as not too long ago as March. And Mr. Powell made it clear that officers wished to see extra encouraging inflation studies earlier than they slashed borrowing prices.
“Readings like in the present day’s are a step in the best course,” he mentioned. “Nevertheless it’s just one studying. You don’t wish to be too motivated by any single knowledge level.”
If officers make just one lower earlier than the top of the yr, it would take their coverage fee to five.1 %. Policymakers gave no clear trace as to when the speed discount may occur. They meet four more times this yr: in July, September, November and December.
For American households, the Fed’s extra cautious method might imply that mortgage charges, bank card charges and auto mortgage charges stay larger for longer. However Mr. Powell emphasised that inflation, too, is painful for households, and that the Fed’s aim is to crush speedy value will increase.
For President Biden, an extended interval of excessive rates of interest might spell a much less vigorous financial system heading into the November election. The White Home avoids speaking about Fed coverage, as a result of the central financial institution units rates of interest independently so officers could make difficult selections with out bowing to short-term political stress. However some Democrats in Congress are loudly calling for fee cuts, and incumbent presidents typically desire decrease rates of interest.
Mr. Biden has come near commenting on Fed coverage at occasions, however has averted placing outright stress on the Fed.
On the flip aspect, whichever presidential candidate wins may benefit from a steeper path of fee cuts subsequent yr: Whilst Fed officers predicted fewer cuts in 2024, they urged that they might scale back rates of interest 4 occasions in 2025, up from three beforehand.
The Fed’s forecasts additionally confirmed that officers count on inflation to show stickier than they beforehand anticipated in 2024: Total inflation might finish the yr at 2.6 %, they predicted, up from 2.4 % of their earlier estimate. Mr. Powell urged that the Fed’s inflation forecasts had been “conservative” ones.
He additionally made it clear that the Fed’s forecasts weren’t a agency plan. If inflation comes down or if the job market takes an surprising flip towards weak point, the Fed might react by reducing rates of interest.
“We don’t suppose that it is going to be applicable to start to loosen coverage till we’re extra assured that inflation is shifting down,” Mr. Powell mentioned, or except there may be an “surprising deterioration” within the labor market.
For now, the financial system stays resilient, and the Fed has only one assembly this summer time, in July. Few buyers count on any motion then.
“I believe this leaves charges in a higher-for-longer sample,” mentioned Blerina Uruci, chief U.S. economist at T. Rowe Value.
RELATED POSTS
View all